MVP Software Development Services
Achieve product-market fit with a minimum viable product that actually solves a problem. Avoid unexpected delays and costs, and launch faster.
Book a CallNo commitment, learn how we can help you launch faster
Custom MVP Software Development Services
Avoid feature overload. Focus on what matters most. Here's how we can help you.
Our Industries Expertise
We love to build products for different industries. Here are some of the industries we have worked with.
Finance
We build MVPs for finance companies to help them to solve problems in their industry.
E-commerce
Build high converting e-commerce MVPs that help you to sell more.
B2B SaaS
Our services help you to build B2B SaaS MVPs that help you to grow your business.
We build custom MVPs for
From small businesses to large enterprises, we build custom MVPs with individual approach.
Small Businesses
We focus on cost, time-to-market, and product-market fit.
Mid/Large Enterprises
We focus on safety, security, scalability and UI/UX.
Startups
We help you to build a product that people love. And deliver it to the market as fast as possible.
How the process looks like?
Here is the overview of the process. We work with you to understand your vision, goals, and requirements for the MVP.
Result you can expect
Achieving Product-Market Fit
We help you to achieve product-market fit.
Fast Time-to-Market
We focus on fast speed of delivery.
Constant updates
We help you to improve the product based on the feedback from the users.
Scalable and Flexible
We build scalable and flexible MVPs that can be easily maintained and scaled.
Case Studies
Explore our recent projects and discover how we've helped businesses achieve their goals through innovative digital solutions
View Case Study
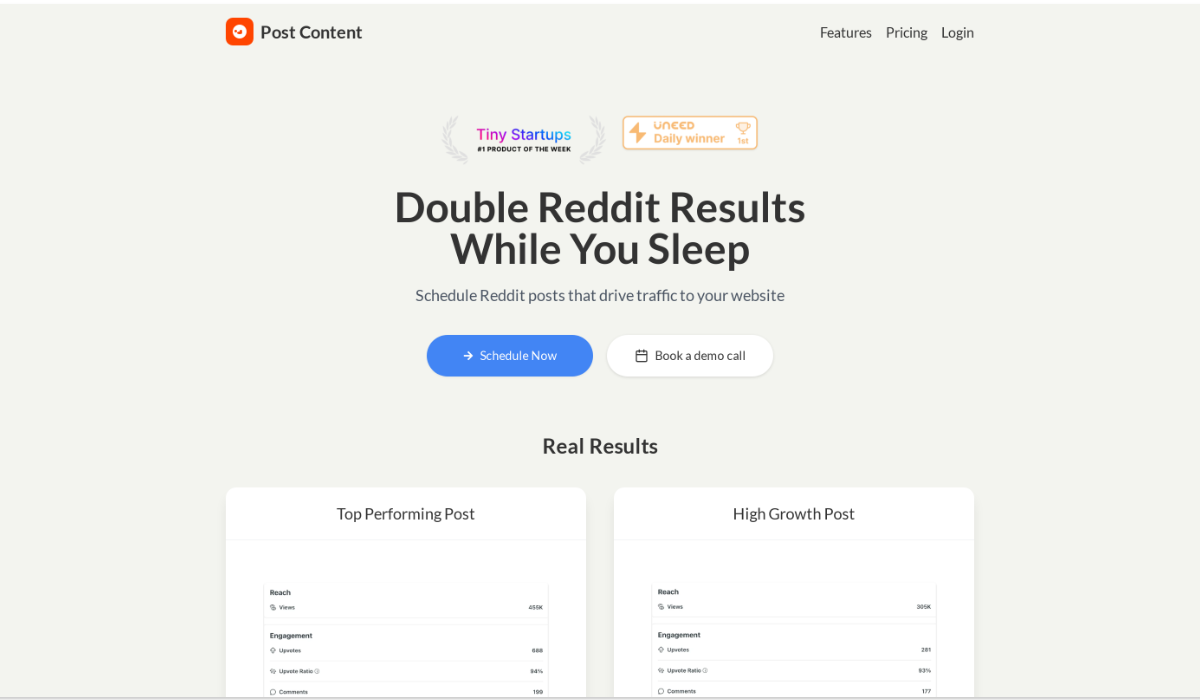
Post Content
Double Reddit Results While You Sleep. Schedule Reddit posts that drive traffic to your website
View Case Study
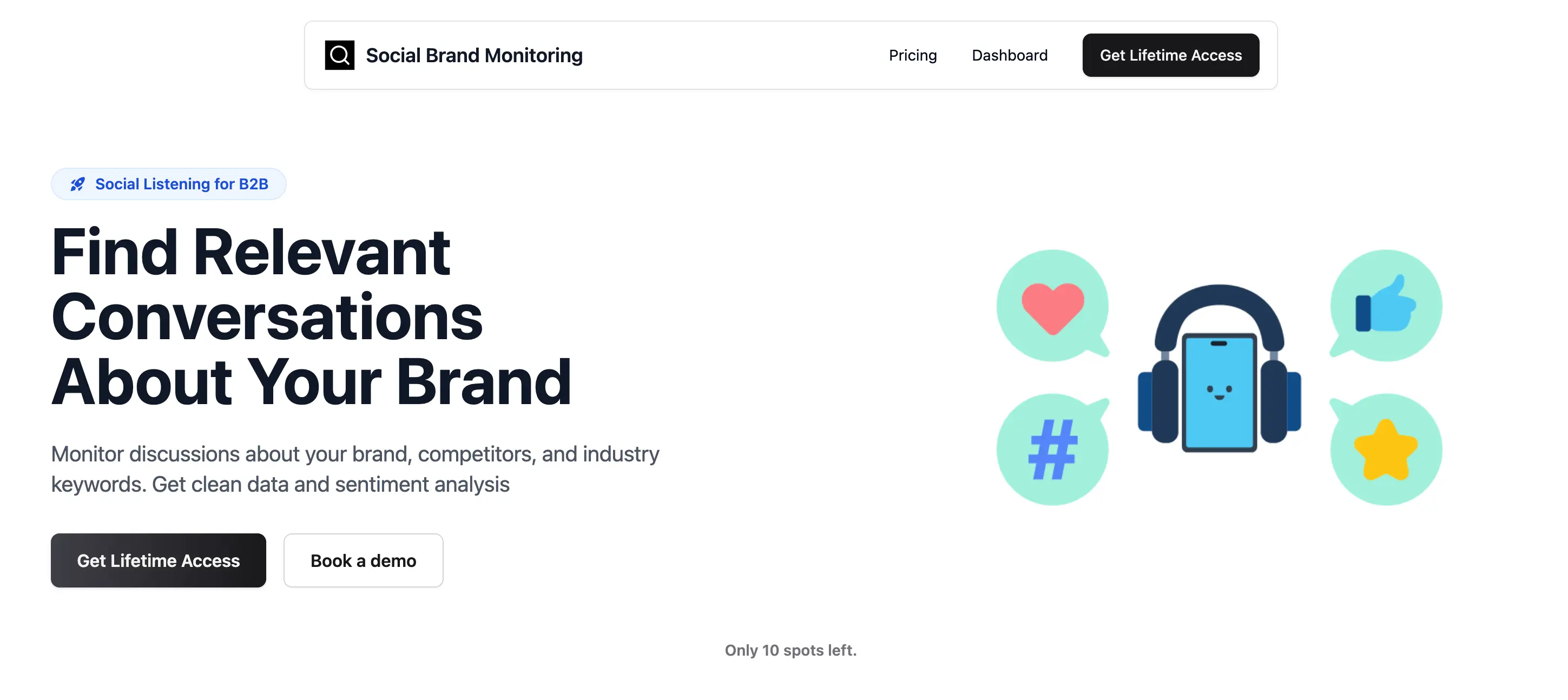
Social Brand Monitoring
Find Relevant Conversations About Your Brand. Monitor discussions about your brand, competitors, and industry keywords.
View Case Study
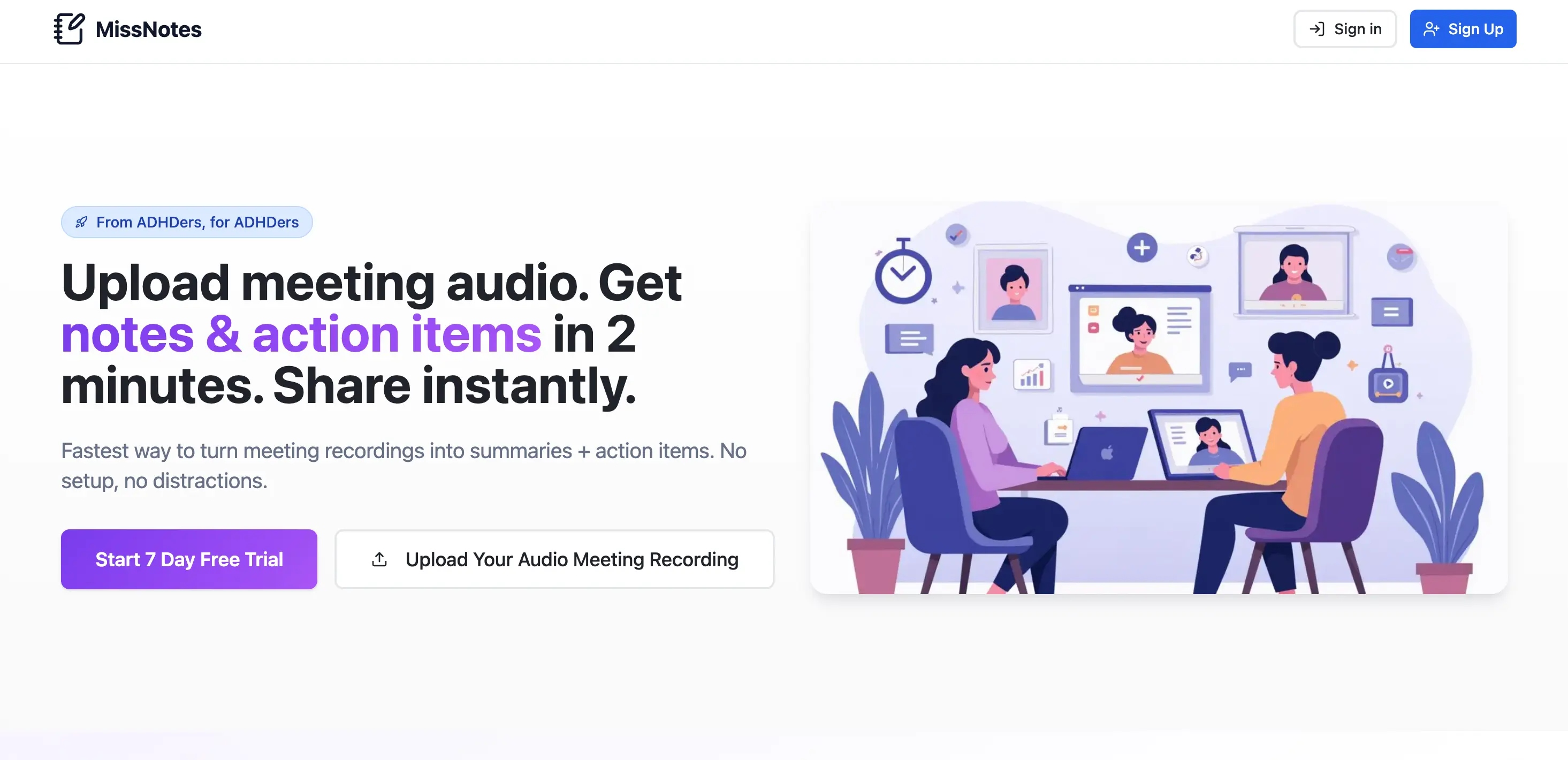
MissNotes
Upload meeting audio. Get notes & action items in 2 minutes. Share instantly.
Simple, Transparent Pricing
Launch your MVP in weeks, not months. No hidden fees.
Growth MVP
$5000
one-timeEverything you need to launch your MVP fast
- Web application development
- Clean, responsive landing page
- Main integrations (Auth, DB, Analytics)
- Payment integration
- Hosting and deployment setup
- SEO Optimization
- Branding and UI/UX
Ongoing Partnership
Contact Us
Customized support and development for your growing product
- Continuous development and maintenance
- Development iterations
- Weekly product updates
- Bug fixes and support
- Perfomance monitoring & control
- IT Infrastructure management
- Improving planning
What Our Clients Say
We don't have a lot of reviews yet,
but here are reviews from businesses that use our apps.
Frequently Asked Questions
We provide a fixed price for MVP development based on the complexity of the project.
On average, it takes 2-4 weeks instead of months of average MVP development agencies.
Book a call with us and tell us about your idea. We will discuss the details and provide a quote.
Yes, we can work with your in-house team. We can help you to build the MVP and continue to work with you to improve the product.








